MEDICINE
MEDICINE
PMDK (REG&INT CLASS) MEDICINE UI 98 (MD)
ANESTHESIOLOGY NATURAL (60)
SAYANG SAYANG LAWAN JENIS (SA WFSA)
3 Moslem fundamental(MF)&FASHION SCORE 10
IP BORN (IPA BDG-JKT) GOLD GALAXY/IPI GOLD GALAXY (KELAHIRAN-AKTA/SKL)/IP BORN CLASS ASSOCIATION
CORE ADM (UMPTN-USM-EJU)&PMDK-DEGREE SA PSUG E (BACHELOR UP)
ALLAH SWT NOT LATTA UZA MANNA (NO SYIRIK/BERHALA)
FASHION (TERTUTUP BERDERAJAT ILMU)
AN ROOM (HOSPITAL)-SUSTER/AN ROOM (MEDICINE SYSTEM&MEDICINE SLEEP JOURNAL)
SAYANG SAYANG
HUG (HUSBAND-WIFE)

PARTNER
NURSE-DOCTOR

CHILD-ADULT

PHYSICIAN CAREER ANESTHESIOLOGY







`






HEAL MUSIC



ARTICLE/PUBLICATION/JOURNAL REFFRENCE
MEDICINE SYSTEM (SOAP)
Study: Soap and water work best in ridding hands of disease viruses
The Effect of Handwashing at Recommended Times with Water Alone and With Soap on Child Diarrhea in Rural Bangladesh: An Observational Study
Foam soap is not as effective as liquid soap in eliminating hand microbial flora
,Margie Morgan, PhD,Ozlem Equils, MD, FAAP
A Study to Ascertain the Practice of Hand Hygiene among MedicalStudents in Commonwealth of Dominica
Opeyemi Oluwabukola Afolabi1, Esther Olajumoke Adewumi1, Srinivas Medavarapu2*, Temiloluwa Oladoyin Ige1, Oluwaseyi Joy Alao1 and Olufemi Emmanuel Dada11Medical students, Basic Medical Sciences,All Saints University School of Medicine, Roseau, Dominica
Assistant Professor, All Saints University School of Medicine, Roseau, Dominica
PHYSICS MEDICINE (30)
BIOFLUIDS MECHANICS
FLUID PARAMETER
Density
Temperature
Velocity
Pressure
Area of Biofluids Mechanics
What level of fluids pressure are present in human body
Parameter govern of blood in the arteries&venna
Is blood thick than water
How can the fluids dynamics perfomance of the heart can be measured
what are the fluid dynamics effects of disease processes
A fluid is defined as a substance that deforms continuously under application of a shearing stress, regardless of how small the stress is. Blood is a primary example of a biological fluid. Air can also be considered as biological fluid as it flows in lungs and the synovial fluid between the knee joints is also an example of a biological fluid. Types of Fluids[3] Fluids can be classified into four basic types. They are:
- Ideal Fluid
- Real Fluid
- Newtonian Fluid
- Non-Newtonian fluid
An Ideal Fluid is a fluid that has no viscosity, means it will offer
no resistance, pragmatically this type of fluid does not exist. It is
incompressible in nature. Real fluids are compressible in nature. They
offer some resistance and thus have viscosity. All Fluids existing are
real fluids.
A Newtonian Fluid is a fluid whose viscous shear stresses (acting
between different layers of fluid and between the fluid layer and
surface over which it is flowing) are directly proportional to the rate
of change of velocity of the flow of the fluid with respect to the
distance in the transverse direction (distance measured perpendicular to
the flow), also known as velocity gradient. The constant of
proportionality is known as the dynamic viscosity of the fluid denoted
by ‘µ’. The functional relationship between viscous shear stress and
velocity gradient is linear in a Newtonian fluid. This relationship may
be written as :
Where
= viscous shear stress
= dynamic viscosity of the fluid
= velocity gradient across the flow
A Non-Newtonian fluid is a fluid which is different from the
Newtonian fluid as the viscosity of non-Newtonian fluids is dependent on
shear rate or shear rate history. In a non-Newtonian fluid, the
relation between the shear stress and the shear rate is different and
can even be time-dependent (Time Dependent Viscosity). Therefore, a
constant coefficient of viscosity cannot be defined.
Non-Newtonian fluids change their viscosity or flow behavior
under stress. If you apply a force to such fluids, the sudden
application of stress can cause them to get thicker and act like a
solid, or in some cases, it results in the opposite behavior and they
may get runnier than they were before. Removal of the stress causes them
to return to their earlier state.
Not all non-Newtonian Fluids behave in the same way when stress is
applied – some become more solid, others more fluid. Some non-Newtonian
fluids react as a result of the amount of stress applied, while others
react as a result of the length of time that stress is applied.
The generalized power law for all fluids can be written as:
 Where K = flow consistency index
n = Fluid behavior index, n=1 for Newtonian fluids
Where K = flow consistency index
n = Fluid behavior index, n=1 for Newtonian fluids
Reynolds number of the flow is defined as the ratio of inertia forces to viscous forces.
Mathematically it is written as

Where
 = density of fluid
v = velocity of fluid
d = characteristic length
= density of fluid
v = velocity of fluid
d = characteristic length
 = dynamic viscosity of fluid
= dynamic viscosity of fluid
The Reynolds number helps us to predict the transition between
laminar and turbulent flows. Laminar flow is highly organized flow along
streamlines. As velocity increases, flow can become disorganized and
chaotic. This is known as turbulent flow. Laminar flow occurs in flow
environments where Re < 2000. Turbulent flow is present in
circumstances under which Re > 4000. The range of 2000 < Re <
4000 is known as the transition range.
Most blood flow in humans is laminar, having a Re of 300 or less, it is
possible for turbulence to occur at very high flow rates in the
descending aorta, for example, in highly conditioned athletes.
Turbulence is also common in pathological conditions such as heart
murmurs and stenotic heart valves. Stenotic comes from the Greek word
"stenos," meaning narrow. Stenotic means narrowed, and a stenotic heart
valve is one in which the narrowing of the valve is a result of the
plaque formation on the valve.
The Womersley number, or alpha parameter, is another dimensionless parameter like the Prandtl number or Reynolds number
that has been used in the study of fluid dynamics. This parameter
represents a ratio of transient to viscous forces, just as the
Reynolds number represented a ratio of inertial to viscous forces. A
characteristic frequency represents the time dependence of the
parameter. The Womersley number may be written as.:[2]
 Where
Where
 = Womersely Number
r = vessel radius
= Womersely Number
r = vessel radius
 = fundamental frequency
= fundamental frequency
 = kinematic viscosity =
= kinematic viscosity = 
The flow profile becomes blunter near the centerline of the vessel in
high frequency flows, because the inertia forces become more important
than viscous forces. But viscous forces are still important near the
wall as here the velocity of the flow is almost zero due to the effect
of the wall and the no-slip condition. Moreover, it can be shown that
the transient forces become relatively more important than viscous
forces as the animal size increases.[2]
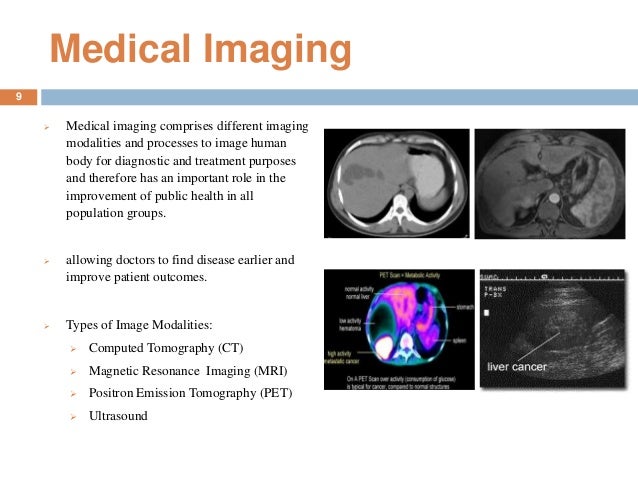
Medical imaging physics is also known as diagnostic and interventional radiology physics. Clinical (both “in-house” and “consulting”) physicists[10] typically deal with areas of testing, optimization, and quality assurance of diagnostic radiology physics areas such as radiographic X-rays, fluoroscopy, mammography, angiography, and computed tomography, as well as non-ionizing radiation modalities such as ultrasound, and MRI
Healthcare Informatics and Computational Physics









- Image processing, display and visualization




- Picture archiving and communication systems (PACS)
- Standards: DICOM, ISO, IHE
- Hospital information systems





- Medicine on the Internet of Things
- Distant monitoring and telehomecare
Physics of the Human Bodies
(1) Biomechanics- Body mass index
- Sports biomechanics
- Biofluid mechanics
- Bioelectrodynamics
- Biomagnetism
- Electromagnetic radiation and health
- Electrophysiology
- Biomaterials for cell and organ therapies
- Cardiovascular biomaterials, artificial heart and cardiac assist devices
- Artificial skin, bones, joints, teeth and related biomaterials
- Histopathology
- Drug delivery and control release
Physiological Measurement Techniques
Physiological measurements have also been used to monitor and measure various physiological parameters. Many physiological measurement techniques are non-invasive and can be used in conjunction with, or as an alternative to, other invasive methods.- Electroencephalography
- Electromyography
- Electronystagmography
- Endoscopy
- Medical ultrasonography
- Non-ionising radiation (lasers, ultraviolet etc.)
- Near infrared spectroscopy
- Pulse oximetry
- Blood gas monitor
- Blood pressure measuremenT
WFSA COURSE MD (JOURNAL ANESTHESIOLOGY) (10)
leads the world in publication of peer-reviewed novel research that transforms clinical practice and fundamental understanding in anesthesiology: the practice of perioperative, critical care, and pain medicine. Anesthesiology is the official journal of the American Society of Anesthesiologists but operates with complete editorial autonomy.
JOURNAL
Association of
perioperative red blood cell transfusions with venous thromboembolism in
a North American registry. JAMA Surg 2018 Jun 13 [Epub ahead of print].
Summary: Martin J. London. Image: J. P. Rathmell.
Unravelling residents’ and supervisors’ workplace interactions: An intersubjectivity study. Med Educ 2018; 52:725–35.
Dabigatran in patients with myocardial injury after non-cardiac surgery (MANAGE): An international, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2018; 391:2325–34.
How do resuscitation teams at top-performing hospitals for in-hospital cardiac arrest succeed? A qualitative study. Circulation 2018; 138:154–63.



Komentar
Posting Komentar